文献速递 | 2020 年 ESC NSTE-ACS 指南系列解读(一)
2020-10-01 00:16:19 贝克曼库尔特商贸(中国)有限公司
文献速递
2020 年 ESC NSTE-ACS 指南
系列解读(一)

推荐要点
※ 本文是最新的欧洲心脏协会(European Society of Cardiology, ESC)关于非 ST 段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征(Non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome, NSTE-ACS)的管理指南,2020 年 8 月 29 日首次发表于《European Heart Journal》杂志。
※ 强调 hs-cTn 初始值(0 h)和变化值(1 h,2 h 或 3 h)在 ACS 中的临床价值。
※ 建议使用 0 h/1 h 算法(首选,在 0 h 和 1 h 进行抽血检测)或 0 h/2 h 算法(次选,在 0 h 和 2 h 进行抽血检测),0 h/3 h 算法可以作为备选。
※ 列举了可能导致 hs-cTn 升高的因素以及急性胸痛鉴别诊断的相关疾病。
主要内容(一)
1. 心肌梗死的通用定义(Universal definition of myocardial infarction):
ESC 2015
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) defines cardiomyocyte necrosis in a clinical setting consistent with acute myocardial ischaemia. A combination of criteria is required to meet the diagnosis of acute MI, namely the detection of an increase and/or decrease of a cardiac biomarker, preferably high-sensitivity cardiac troponin, with at least one value above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit and at least one of the following:
(1) Symptoms of ischaemia.
(2) New or presumed new significant ST-T wave changes or left bundle branch block on 12-lead ECG.
(3) Development of pathological Q waves on ECG.
(4) Imaging evidence of new or presumed new loss of viable myocardium or regional wall motion abnormality.
(5) Intracoronary thrombus detected on angiography or autopsy.
ESC 2020
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) defines cardiomyocyte necrosis in a clinical setting consistent with acute myocardial ischaemia. A combination of criteria is required to meet the diagnosis of AMI, namely the detection of an increase and/or decrease of a cardiac biomarker, preferably high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) T or I, with at least one value above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit and at least one of the following:
(1) Symptoms of myocardial ischaemia.
(2) New ischaemic ECG changes.
(3) Development of pathological Q waves on ECG.
(4) Imaging evidence of loss of viable myocardium or new regional wall motion abnormality in a pattern consistent with an ischaemic aetiology.
(5) Intracoronary thrombus detected on angiography or autopsy.
ESC 2020 关于急性心肌梗死(Acute myocardial infarction,AMI)的界定,几乎没有变化。
2. 肌钙蛋白(Troponin)用于 ACS 的风险分层
ESC 2015
ESC 2020
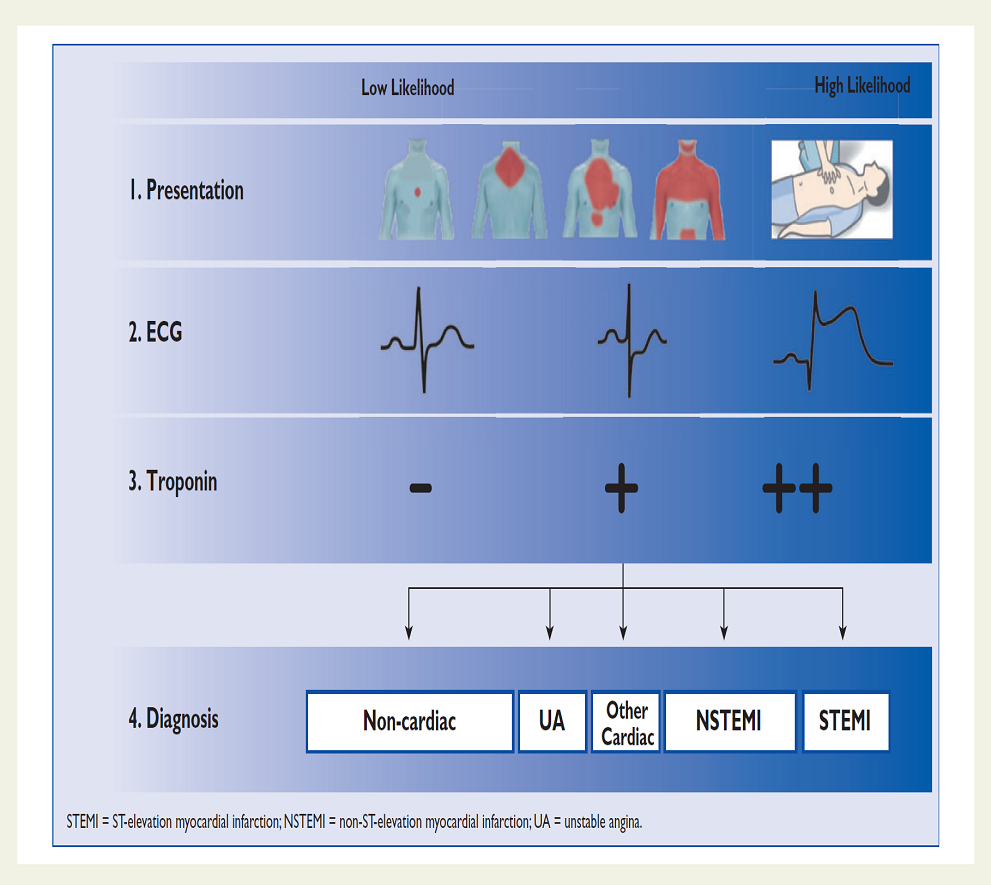
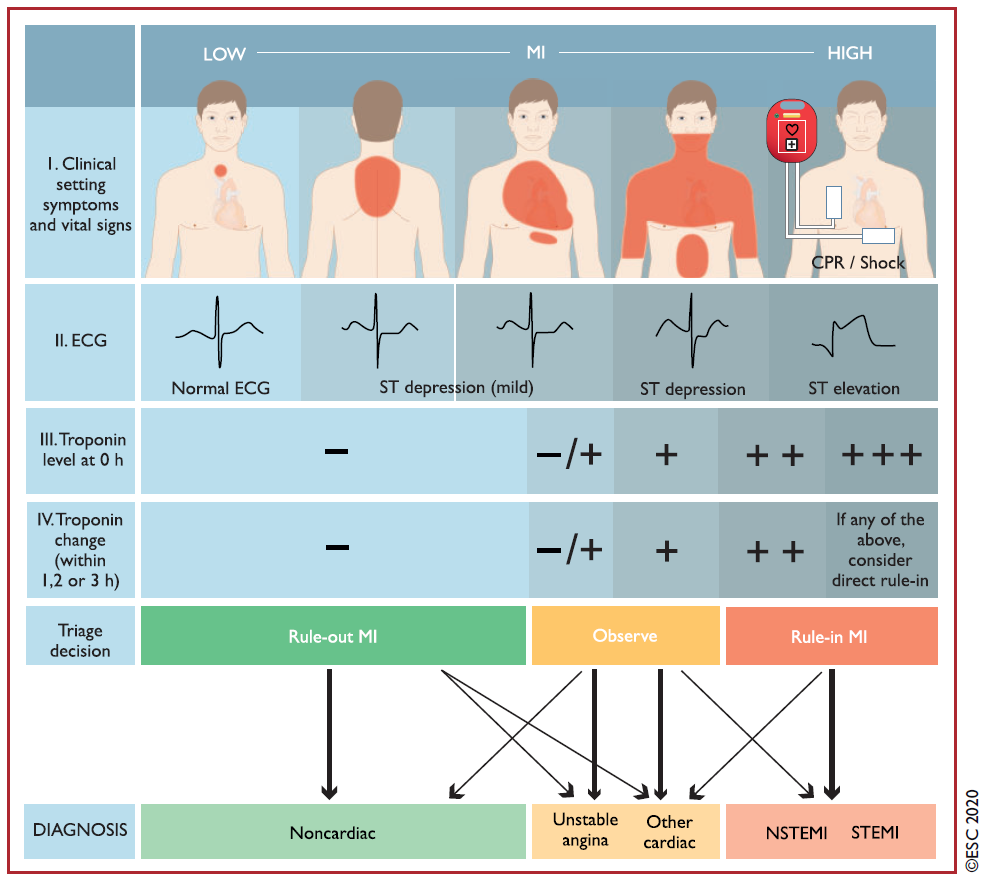
ESC 2020 强调了肌钙蛋白在 ACS 诊疗中的作用:1)不单单强调首次(0 h)hs-cTn 的价值;2)同时强调了 hs-cTn 的变化值的临床价值,这也是 2020 ESC 指南的一个变化点。
3. 高敏肌钙蛋白的价值
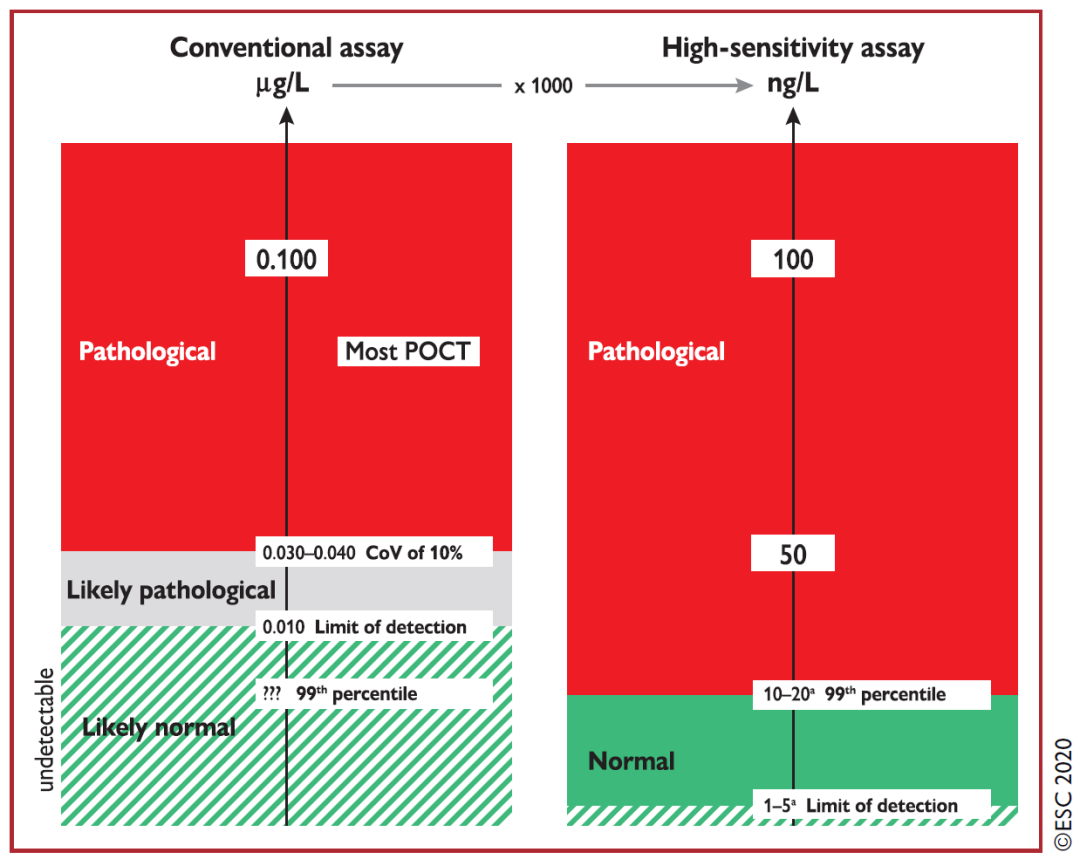
ESC 2020 比较了传统肌钙蛋白(Conventional assay)和高敏肌钙蛋白(high-sensitivity assay,hs-cTn)的不同:1)单位的改变,从 μg/L 更改为 ng/L,相当于乘以 1000 的系数;2)如果 hs-cTn 显著升高(比如 >100ng/L),则提供与传统肌钙蛋白相似的信息;3)hs-cTn 可以在「正常(normal)」和「轻度升高(midly elevated)」之间提供精确的区分,而传统肌钙蛋白(包含 POCT)则无法精确区分;4)之前利用传统肌钙蛋白无法检测出(undectable)的一些患者利用 hs-cTn 则可能超过 AMI 相关的 99th URL。
4. hs-cTn 的临床应用
与传统心肌肌钙蛋白相比,hs-cTn:
• 拥有更高的 AMI NPV(NPV,阴性预测值)。
• 缩短了肌钙蛋白检测不到的时间间隔,从而更早发现 AMI。
• 导致 I 型 MI 的诊断有 4% 的绝对升高和 20% 的相对升高,减少不稳定性心绞痛(UA)的诊断。
• 与 II 型 MI 的诊断增加 2 倍有关。
hs-cTn 水平作为心肌损伤的定量指标(比如 hs-cTn 水平越高,MI 的可能性越大)
• hs-cTn 超过 5 倍 URL(参考范围上限)时,I 型 MI 的 PPV >90%(PPV,阳性预测值)。
• hs-cTn 超过 3 倍 URL 时,AMI 的 PPV 有限(50%~60%),并且可能与多种疾病相关。
• 在健康个体中检测到心肌肌钙蛋白比较普遍。
hs-cTn 的变化(升高或降低),可用于区分急性(比如 MI)和慢性心肌细胞损伤,其变化越明显,AMI 的可能性越大。
5. hs-cTn 与床旁检测(point-of-care tests,POCT)
当前使用的大多数床边即时检验( POCT) 不能被视为敏感或高敏感度的检测手段。POCT 虽然具有明显的时间优势(即更短的周转时间),但是优势被其较低的灵敏度,较低的诊断准确性和较低的阴性预测值(NPV)所抵消。
相关内容:《2020 年 ESC NSTE-ACS 指南系列解读(二)》(见下篇)
参考文献
Collet J P, Thiele H, Barbato E, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation [J]. Eur Heart J, 2020, 0:1-79. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575
07-01 英斯特朗
连载 | 药物一致性评价与粒度分析(三)07-01 欧美克仪器
【仪器百科】LS-909丨干湿二合一激光粒度分析仪07-01 欧美克仪器
标准物质解决方案 | PFASs(全氟及多氟化合物)06-29
第九期阿尔塔有约 | 环境专题【新污染物:PFAS】技术研讨会精彩回顾及提问解答06-29
“绿色技术范式”,分析化学未来发展方向——访中国分析测试协会副理事长、辽宁省分析科学研究院原院长刘成雁教授06-29 转载仪器信息网
华西医院-标准型数显脑立体定位仪、双通道体温维持仪、体式显微镜安装完成06-29 迈越生物
科鉴检测助力2家仪器企业获得首批产品可靠性认证证书06-28 科鉴检测
德国耶拿:锂电池生命周期分析解决方案06-28 德国耶拿
AI已来!生命科学本科教学如何紧跟技术浪潮06-28 Opentrons
盛瀚售后,五星级服务的秘诀是什么?06-28 SHINE
专为汽车制造商打造的柔性解决方案——实现制程控制06-28
西北工业大学-脑立体定位仪安装完成06-28 迈越生物
会议邀请 | 第九届海上检验医师论坛06-28
卓立要闻 | 创新发展ing…6月卓立“大事小情”速览06-28 光电行业都会关注
打造信任合作伙伴!2024年度卓立汉光客户满意度调查开启06-28 光电行业都会关注
如何挑选适用于三阶光学非线性的测量系统?Z扫描测量系统来助力!06-28 光电行业都会关注
招聘启事—中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所微纳光学测量表征技术课题组06-28 光电行业都会关注
谱育科技作为主要完成方 荣获2023年度国家科学技术进步一等奖和二等奖06-28 点击关注→
仪器原理丨顶空仪与吹扫捕集仪科普小知识06-28 天美色谱