诚信认证:
工商注册信息已核实! 扫一扫即可访问手机版展台
扫一扫即可访问手机版展台
蛋白质组学就是这么NB(IF43):揭示植物与细菌之间的共生机制!
Nature Biotechnology IF=43.113
定量蛋白质组学与翻译后修饰研究共同揭示豆科植物共生固氮机理
A proteomic atlas of the legume Medicago truncatula and its nitrogen-fixing
endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti
研究背景:生物固氮作用是生态圈氮循环中重要的一环,豆科植物的固氮机理也是农业与植物科学研究的热点。早期已经从转录组学和基因组学层面对豆科模式植物苜蓿进行了一些基础研究,本文则是联合多组学分析深入解析了苜蓿与根瘤菌共生固氮机理。
样本来源:根、茎、叶、花、种子、顶端分生组织以及不同发育阶段的根瘤,来源于接种中华根瘤菌(Sinorhizobium meliloti)的截形苜蓿(Medicago truncatula cv. Jemalong A17)。
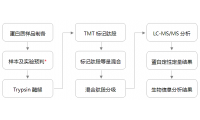
技术:Label-free定量蛋白质组学+TMT修饰蛋白质组学(磷酸化、乙酰化)
研究结果:
1、对感染根瘤菌苜蓿的七个部位(根、茎、叶、花、种子、顶端分生组织以及不同发育阶段的根瘤)分别取样进行蛋白组学分析(label-free),共检测到23,013个蛋白质(苜蓿19,679个,根瘤菌3,334个);修饰蛋白组学分析发现20,120个磷酸化位点和734个乙酰化位点(TMT修饰组学)。


2、不同部位以及根瘤发育不同阶段蛋白质组学,修饰蛋白质组学数据整合分析得到全局蛋白表达图谱:环形蛋白质组学图谱(circular proteome maps,CPM);比较分析发现有一批核心蛋白质组(core proteome,5,701个蛋白)在苜蓿所有部位均高表达,而且翻译后修饰位点也较为集中于这些核心蛋白质组。
环形蛋白质组学图谱(circular proteome maps,CPM)

 Figure 1 In-depth proteome sequencing reveals organ-specific proteins and post-translational modifications. (a,b) Circular proteome maps depict the similarities and differences in the organ-specific proteomes acquired following proteome analysis of seven M. truncatula organs (apical meristem, flower, leaf, root, seed, stem, and nodules 10, 14, and 28 d past infection) (a) and nodule rhizobia (10, 14, and 28 d past infection) (b). The number of protein identifications associated with each organ is displayed by heat maps. The color gradient within these heat maps and respective links reflect the number of organs each protein identification is associated with, where the lightest green region represents the core proteome. The relative abundance of each protein within a given organ is represented by the black histograms. Organ-specific proteins, phosphorylation sites, and lysine acetylation sites are indicated by the red, blue, and purple histograms, respectively. Note that the length of each bar reflects the organ specificity of each protein or PTM site, i.e., longer bars represent a greater degree of specificity.
Figure 1 In-depth proteome sequencing reveals organ-specific proteins and post-translational modifications. (a,b) Circular proteome maps depict the similarities and differences in the organ-specific proteomes acquired following proteome analysis of seven M. truncatula organs (apical meristem, flower, leaf, root, seed, stem, and nodules 10, 14, and 28 d past infection) (a) and nodule rhizobia (10, 14, and 28 d past infection) (b). The number of protein identifications associated with each organ is displayed by heat maps. The color gradient within these heat maps and respective links reflect the number of organs each protein identification is associated with, where the lightest green region represents the core proteome. The relative abundance of each protein within a given organ is represented by the black histograms. Organ-specific proteins, phosphorylation sites, and lysine acetylation sites are indicated by the red, blue, and purple histograms, respectively. Note that the length of each bar reflects the organ specificity of each protein or PTM site, i.e., longer bars represent a greater degree of specificity.
3、本文利用方差分析、层次聚类以及基因本体富集分析对蛋白共表达,修饰共调控机制,蛋白域,未鉴定蛋白功能以及未知基因产物推测等进行了深入分析。

 Figure 2 Functional characterization of proteins and post-translational modifications in M. truncatula. Heat maps are composed of proteins, phospho-isoforms and lysine acetyl-isoforms significantly changing (FDR q < 0.01, ANOVA) between six M. truncatula organs (n = 4,765, n = 11,101 and n = 234, respectively). Expression data were grouped by hierarchical clustering, both on the organ level and on the protein/PTM-isoform level. For each data set, proteins/PTM-isoforms were grouped into 12 clusters, each of which was subjected to gene ontology (GO) enrichment (FDR q < 0.01, Fisher’s exact test). Each heat map is associated with the top GO terms (right) significantly enriched within select clusters. Expression profiles (left) depict co-expressed and co-regulated (uncharacterized) proteins. Uncharacterized proteins and assigned PFAM domains are highlighted by WMG accession.
Figure 2 Functional characterization of proteins and post-translational modifications in M. truncatula. Heat maps are composed of proteins, phospho-isoforms and lysine acetyl-isoforms significantly changing (FDR q < 0.01, ANOVA) between six M. truncatula organs (n = 4,765, n = 11,101 and n = 234, respectively). Expression data were grouped by hierarchical clustering, both on the organ level and on the protein/PTM-isoform level. For each data set, proteins/PTM-isoforms were grouped into 12 clusters, each of which was subjected to gene ontology (GO) enrichment (FDR q < 0.01, Fisher’s exact test). Each heat map is associated with the top GO terms (right) significantly enriched within select clusters. Expression profiles (left) depict co-expressed and co-regulated (uncharacterized) proteins. Uncharacterized proteins and assigned PFAM domains are highlighted by WMG accession.
3、利用统计分析火山图发现在根瘤生长过程中许多根瘤功能相关蛋白差异表达,这些蛋白的磷酸化修饰也发生了变化(Figure 3a);文中利用转录组数据构建蛋白表达网络对蛋白调控关系进行预测分析;在重点关注结瘤过程蛋白网络图谱中,他们发现一类钙调素结合蛋白(calmodulin-binding protein)具有最高的连通程度(Figure 3b),推测其在共生体的调节与维持过程中发挥核心作用。
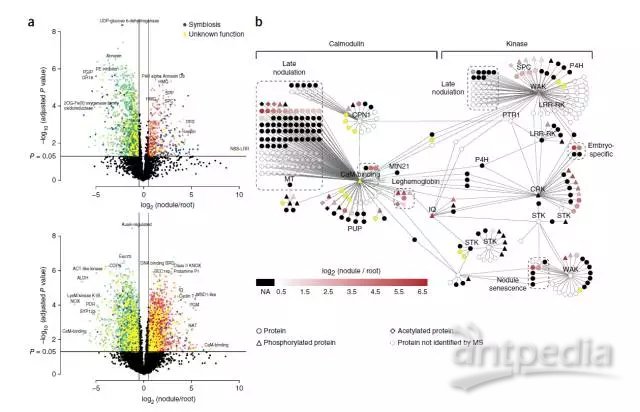
Figure 3 Nodule-specific proteins and post-translational modifications provide evidence for key regulators in symbiosis. (a) Volcano plots compare protein (top) and phospho-isoform (bottom) expression in nodules to root organs, indicating known proteins key to symbiosis, proteins of unknown function and candidates with a putative role in symbiosis. Known symbiosis proteins encompass processes such as nodule senescence, oxygen transport, and immune response, among others. (b) A nodule-specific sub-network was extracted from our global transcript co-expression network by mapping significantly (FDR q < 0.01, Student’s t-test) upregulated proteins and motifs from (a) to the network. The sub-network is organized based on the classification of hub genes, which were either calmodulin-like/calmodulin-binding or kinases. The color of each node reflects the fold-change from (a). Select gene families have been illustrated by dashed boxes. Genes not identified by our protein analysis have been faded.
4、对结瘤特异性的半胱氨酸富含蛋白(NCR)在根瘤发育过程中的表达模式进行统计分析发现NCR在结瘤过程中发挥重要功能:早期调控根瘤形态发生,后期调控共生体形成(Figure 4a)。进一步分析根瘤生长过程中根瘤菌蛋白表达情况找到了NCR的靶向蛋白:转录调节因子,细胞分裂相关蛋白以及RNA聚合酶辅助因子等(Figure 4b)。

 Figure 4 Temporal stages of host-factor expression in M. truncatula and putative targets in S. meliloti. (a) Host factor time-course profiles obtained from the deep sequencing (LFQ) analysis (n = 252) were grouped by hierarchical (left) and fuzzy c-means clustering (right). Expression profiles were pairwise correlated (Pearson), clustered (hierarchical) by correlation coefficients and reordered by fuzzy clusters. Darker trace colors reflect stronger membership to the given fuzzy cluster. (b) S. meliloti downregulated (more than twofold) proteins from 10–28 d past rhizobial infection were gene ontology enriched (FDR q ≤ 0.05, Fisher’s exact test), extracted (shown along border) and mapped to their corresponding protein-protein interactions (STRING database, shown within inner network circle). The size of each protein node reflects its degree within the network and the color of each node reflects how its protein expression changed over the 18-day time course.
Figure 4 Temporal stages of host-factor expression in M. truncatula and putative targets in S. meliloti. (a) Host factor time-course profiles obtained from the deep sequencing (LFQ) analysis (n = 252) were grouped by hierarchical (left) and fuzzy c-means clustering (right). Expression profiles were pairwise correlated (Pearson), clustered (hierarchical) by correlation coefficients and reordered by fuzzy clusters. Darker trace colors reflect stronger membership to the given fuzzy cluster. (b) S. meliloti downregulated (more than twofold) proteins from 10–28 d past rhizobial infection were gene ontology enriched (FDR q ≤ 0.05, Fisher’s exact test), extracted (shown along border) and mapped to their corresponding protein-protein interactions (STRING database, shown within inner network circle). The size of each protein node reflects its degree within the network and the color of each node reflects how its protein expression changed over the 18-day time course.
5、此外,作者还鉴定到了许多的短肽(<20个氨基酸),这些短肽在植物生长调节、免疫应答以及共生作用中发挥重要的功能;作者认为深入研究这些多肽将有助于解析共生固氮的机理。
小编心得:
本文是一篇非常精彩的多组学联合分析的文章(涉及到基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和修饰蛋白质组学)。在已有的苜蓿基因组和转录组数据的基础上对苜蓿的近乎所有部位(根、茎、叶、花、种子、顶端分生组织以及不同发育阶段的根瘤)蛋白质组和修饰蛋白质组进行测序。整合转录组、蛋白质组和修饰蛋白质组数据进行联合分析,鉴定到了苜蓿核心蛋白质组(多部位共表达蛋白子集)和根瘤蛋白质组(参与根瘤生长及调控的特异蛋白子集);在此基础上建立共生固氮调控网络,发现核心蛋白。他们的成果必然会对根瘤固氮机理研究起到巨大的推进作用。点赞!
中科新生命 · 质谱系统解决方案专家
▼
生物医药结构确证
蛋白质组 - 修饰蛋白质组 - 代谢组 - 脂质组
▼
技术支持
公众号 · 行业动态
www.aptbiotech.com T: 021-54665263 E: info_apt@sibs.ac.cn Q: 1875681852